ENVIRONMENT
Since its establishment, PVCFC has always focused on building an environmental management and control system. The Company strictly complies with regulations on safety, firefighting and prevention and environment such as: building an online monitoring system to continuously monitor and track the plant's emission activities and transmit data to the Department of Natural Resources and Environment for management and supervision; quarterly environmental monitoring results are publicly posted on the Company's website in the QHSE section. Management methods and environmental performance index for each specific content are described as below.

It is mandatory for manufacturing plants in general and Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant in particular to sue water source (boiler feedwater for steam production, open circulating cooling river water through the tower cooling system). cooling, fresh water for closed circulation cooling, etc.) to serve requirements of production technology. In addition, daily activities still generate domestic wastewater depending on the needs.
PVCFC always controls and manages clean water and river water usage, ensuring savings and efficiency. The Company also focuses on building and complying with wastewater treatment processes to ensure quality before returning source, preventing environmental pollution and affecting biodiversity in the locality.
WATER EXPLOITATION AND DISCHARGE
Water for cooling purposes takes the biggest amount generated from river water, less polluted during production processes, ensuring quality before returning to the source.
Total amount of river water exploited in 2023 was 16.45 million m³ and 15.08 million m³ in 2022. Total amount of water supplied was 1.2 million m³ and 1.14 million m³ in 2023 and 2022 respectively; total amount of wastewater generated was 11.97 million m³ and 11.8 million m³ in 2023 and 2022 respectively. Total amount of river water exploited and total amount of wastewater generated at Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant are within the allowed limits eligible for exploitation and discharge, as licensed by State management agencies.
Total amount of river water exploited in 2022 was
15.08 million m3
Total amount of river water exploited in 2023
16.45 million m3
2022
1.14
million m3
2023
1.2
million m3

2022
11.8
million m3
2023
11.97
million m3
QUALITY CONTROL OF WASTEWATER
We, at Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant, always maintain continuous operation of domestic & oily wastewater treatment systems and other wastewater systems at 24/24; deploying continuous environmental monitoring system to control quality of wastewater discharged into the environment and compliance with QCVN as follows:
- Output of domestic wastewater treatment system: monitoring parameters such as: pH, BOD5, TSS, TDS, Surfactants, animal fats and vegetable oils, Sulphide, Ammonium, total phosphorus, total nitrogen , Coliform, Flow, compliance with QCVN 14/2008/BTNMT.
- Output of oily wastewater treatment system and output of ammonia wastewater treatment system: monitoring parameters: pH, Color, BOD5, COD, Suspended solids, Arsenic, Mercury, Lead, Cadmium, Iron, Copper, total and mineral oil and grease, Sulphide, Ammonium, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, residual chlorine, Coliform, wastewater flow, compliance with QCVN 40:2011/BTNMT.
- Common output of 03 oily, ammonia and domestic wastewater treatment systems and common drainage channel: monitoring parameters: temperature, color, pH, BOD5, COD, TSS, Total dissolved solids (TDS), Arsenic, Mercury, Lead, Cadmium, Copper, Iron, total and mineral oil and grease, total surfactants, animal fats and vegetable oils, Sulphide, Ammonium (as Nitrogen), total Nitrogen, total phosphorus, residual chlorine, Coliform, compliance with QCVN: 40:2011/BTNMT
- Waste cooling river water output: monitoring parameters: pH, temperature, residual Chlorine, in accordance with QCVN: 40:2011/BTNMT.
REDUCTION OF WATER CONSUMPTION
Thanks to water saving measures and awareness of each employee, water consumption per ton of product in 2023 was reduced by 0.15%. It is expected that by the end of 2024, we will launch the resource recovery project from the existing RO system. As estimated, this can help save up to 4.1 billion VND annually and reduce the amount of chemicals used for water treatment system.

Fertilizer manufacturing technology in general and of Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant in particular have the characteristics of using natural gas (fossil energy). Therefore, PVCFC always pays special attention to greenhouse gas emissions and global warming. The company constantly improves technical requirements, optimizing fuel sources, seeking new breakthrough solutions to save energy and improve production capacity, reducing greenhouse gas emissions of Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant.
There are 2 concerned issues regarding natural gas consumption of Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant including raw natural gas and fuel combustion. With characteristics of technology, gas combustion provides heat required for exceed steam for reforming and gas for auxiliary boilers providing high-pressure steam is still consumable gas for steam purposes used in technology cycle of the plant. In 2022, permeate gas as raw material fuel is recovered for burning, however, in 2023, we used permeate gas with 100% CO₂ recovery and the rest after meeting requirements of technology as production materials with an amount of permeate gas of 19.96 million Sm³/year in 2023. Additionally, we have applied solutions to enhance the output and reduce consumable gas by 0.44% as of 2022.
| Solutions | Time of putting into operation | Technical efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Recovering permeate gas as material fuel | 2019-present | Amount of recovered permeate gas: 18.35 million Sm³ (2022) and 19.96 Sm³ (2023) |
| Replacing distribution systems of Towers S04301, S04302, C04301 | September 2022 | Expanding the overall capacity of CO₂ separation cluster, reducing the amount of output CO₂ slip at absorber towers, increasing capacity of NH₃ to 5.4 tons/day. |
| Separating flash gas & using output washed gas C0403 as production material | November 2022 | Increasing capacity of NH₃ to 7.1 tons/day. |
| Recovering hydrogen Offgas stream |
Phase 1: December 2021 Phase 2: November 2022 |
Increasing capacity of NH₃ to 18 tons/day. |
| Installing E04212C to optimize the Low temperature CO converter R04205 | November 2022 | Increasing capacity of NH₃ to 4.4 tons/day. |
In 2023, given the “ceaseless efforts”, Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant maintained continuous and stable operation in more than 350 days without any machine downtime. These results have been certified by Haldor Topsoe. In addition, Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant has also been certified by Toyo Engineering company (TEC)for its record of maintaining continuous and stable operation of a granulation workshop in 45 days using TOYO urea granulation technology. Efforts in maintaining continuous operation have helped PVCFC reduce a significant amount of gas emissions.
We have been implementing “green” projects and will put into operation in the future toward application of renewable and green energy:
- Project of rooftop solar power & renewable energy at Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant
- Projects of integrating green hydrogen and renewable energy production from electrolysis technologies
- Project of recovering CO₂ in existing natural gas to reduce CO₂ emissions
- Project of recovering CO₂ in furnace smoke from technology clusters.
PVCFC always considers climate change as a serious issue that needs to be the most concerned in Vietnam and around the world. Reduction of climate change impact is an important and necessary task in the business and production process. Therefore, PVCFC has built management policies and procedures of business and production activities to minimize impacts on climate change. The Company has focused on evaluating environmental impacts since early days of putting into operation (2011). These efforts are shown in its procedures of ensuring compliance, consistency and dissemination to each employee of PVCFC.
Greenhouse gas report
PVCFC always and seriously complies with regulations on greenhouse gas reports. As a fertilizer manufacturer, PVCFC implements its report in compliance with Decree No 06/2022/ND-CP of the Government on regulations of minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and protecting Ozone layer, Circular No 38/2022/3 TT-BCT on measuring, reporting, appraising reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and greenhouse gas inventory for trade and industry. In 2023, we have inspected, collected evaluation information according to the following instructions:
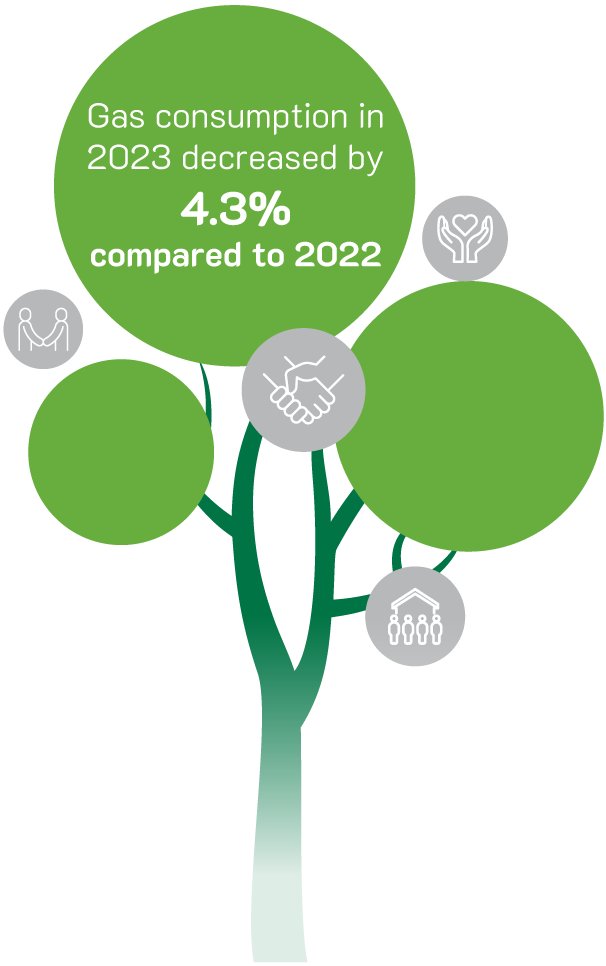
In 2022, directly-burned fuel for the technology system included fuel for auxiliary boiler, reforming and flare system. Total amount of gas consumed in 2023 (555.98 million Sm³/year), up 3.42% as of 2022 (357.57 million Sm³/year). Gas consumption in 2023 reached 35.484 GJ/ton NH₃, down 4.3% as of 2022 (35.648/T.NH₃). This clearly shows that PVCFC pays special attention to minimize CO₂ emissions and gas consumption. PVCFC has not implemented greenhouse CO₂ emissions report covering all scopes but its efforts in reviewing data and statistics have been implemented every year by following bases:
- Electricity emissions: according to Announcement of Climate Change Department, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment dated December 31 2021, the emissions coefficient of Vietnam’s power grid in 2022 is 0.7221 tCO₂/MWh
- Natural gas (1,000 m³) according to IPCC: 2.114 tCO₂/unit
- DO (1000 liters) according to IPCC: 2.73 tCO₂/unit
- A92, A93 gasoline (1,000 liters) 2.408 tCO₂/unit
| Emission activities | Unit | 2022 | 2023 | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emission intensity | Ton CO₂/ ton of products | 0.5463 | 0.5433 | Decreased 0.56% |
| Total of emissions (A+B) | Ton CO2/year | 501,395.5 | 515,635.3 | Increased 2.84% |
| A. Direct emissions (1 + 2) | Ton CO2/year | 380,996.82 | 392,803.5 | Increased 3.1% |
| 1. Burning fuel | Ton CO2/year | 379,729.98 | 391,404.74 | Increased 3.07% |
| Natural gas | Ton CO2/year | 340,928.5 | 352,603.31 | |
| Permeate gas | Ton CO2/year | 38,801.4 | - 38,801.4 | |
| 2. Fuel used for shuttle bus service | Ton CO2/year | 1,266.8 | 1,398.7 | Increased 10.41% |
| DO oil | Ton CO2/year | 409.91 | 872.5 | |
| A92, A95 gasoline | Ton CO2/year | 856.93 | 526.23 | |
| B. Indirect emissions | Ton CO2/year | 120,398.7 | 122,831.9 | Increased 2.02% |
| Power consumed | Ton CO2/year | 120,398.7 | 122,831.9 |
As currently calculated, total amount of gas emissions in 2023 increased by 2.84% but emission intensity/ton of products reduced by 0.56%. This shows the efficiency of solutions on gas emissions at Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant.
Solutions to climate change
In 2023, PVCFC has planted 300,000 green trees, contributing 1 million green trees to the Government toward Net Zero emissions by 2030.
Additionally, PVCFC has effectively implemented the process of energy transition and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. In 2023, PVCFC has established a Steering Committee for energy transition and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions to assign clear functions and tasks for each team, individual; working out implementation plans for projects including: integrated CO₂ in food processing system, recovery of CO₂ from separating CO₂ from fuel gas (containing 8% CO₂), recovery CO₂ from reforming furnace smoke, rooftop solar energy of 5 MWh at Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant, etc.
Additionally, we have worked out short-term and long-term plans to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in the period of 2023-2030, expected to reduce 60,000 tons of CO2/year.

The company always complies regulations of the Law on discharge of sewage. All gas emissions of the plant are closely controlled in both quantity and quality, ensuring compliance with requirements and standards before discharging into the environment:
- Emissions monitoring locations: primary reforming chimney; auxiliary boiler chimney; granulation chimney with monitoring parameters: dust, CO, Nox, NH₃, noise, vibration. According to QCVN 19/2009/BTNMT; 21/2009/BTNMT.
- Periodic monitoring results in 2023 at all monitoring locations are within the allowed limit. Apart from conducting periodic monitoring, PVCFC has also installed automatic monitoring systems to continuously monitor gas emissions and parameters including: emissions at the granulation chimney: flow, pressure, dust, temperature and NH₃; emissions at Ammoniac chimney: temperature, flow, pressure, dust, Nox, SO₂; emissions at NPK chimney: temperature, pressure, dust.
- Automatic monitoring data is continuously received with a frequency of 5 minutes/data and directly transmitted to Ca Mau Department of Natural Resources and Environment
Types of energy consumed
Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant uses the two most important energy sources including natural gas and electricity. As we may know, gas is a non-renewable source and the riskiest factor in case of lacking production gas at the plant in particular and Ca Mau Fertilizer Gas Power Industrial Complex in general. In recent years, the plant has been renovated to increase its capacity to 115.5%. This requires an increasing source of gas while it is not easy to find alternative gas. Being aware of this, in early 2023, PVCFC has decided to establish a working group and conduct research on solutions and commercial legality to diversify its long-term gas for sustainable development of PVCFC.
Emery management techniques
On a yearly basis, PVCFC sets up regulations on economic-technical norms to direct and urge Production Operation Division to seek solutions to reduce energy consumption. Additionally, in order to strengthen activities under National Energy Efficiency Program 2019-2030, PVCFC has considered, reviewed and worked out approval planning for 2019-2030 period with 2 key group of tasks:
Group of tasks No 1: Energy saving. Accordingly, PVCFC has set up solutions on controlling and complying with economic-technical norms of the Company: controlling annual energy consumption and saving.
Technology initiatives from 2022 have contributed to reduction of CO₂ emissions of PVCFC as follows:
- MP vent gas recovery system at Urea factory as reforming fuel helps reduce energy consumption by 4.81 GJ/h and partly reduce greenhouse gas CO₂.
- Replacing SuperCups Trays by reactor R06101 helps increase operational stability at high load and increase conversion efficiency by 0.75% and saves energy by about 6.86 GJ/h
- In July 2023, we officially operated the ORC system, taking advantage of excess heat to generate power with an operational capacity of 113kWh. Till end of 2023, PVCFC has reduced 425.28 MW/year of consumable power and amount of CO₂ emissions at the natural gas-powered electricity factory.
Group of task No 2: Enhancing capacity according to strategic goal by 2025, increasing operational capacity by 115%.
Since being put into operation, Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant always maintains a capacity of 110%, 1% higher than that of other plants (109%) or even up to 115.5% in 2023 regarding operational capacity. The amount of energy consumption at Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant was quite low. In 2022, Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant was honored as a " Top 10% factories with the lowest energy consumption in the world” and Top 10% global factories by capacity by Haldor Topsoe.
In 2023, PVCFC issued an energy management model, reviewing energy management policies to make it more effective toward an energy management model according to ISO 50001:2018. In order to seek optimal solutions, PVCFC has registered for Vietnam-Denmark Energy Partnership Program Phase 3 (DEPP3) for the period of 2020-2025 to promote energy efficiency in various industries by building and piloting Voluntary Agreement Program, building capacity for enterprises with large energy consumption in Vietnam.
Energy consumption results in 2023
According to the business and production plan by 2025 approved by Resolution No. 6395/NQ-DKVN of Vietnam Oil and Gas Group, Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant by 2025 will strive to reduce 5% of energy consumption as of 2022. After a process of continuous renovation and production optimization, Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant in 2023 has reduced 4.23% of energy consumption as of 2022.
2023 energy consumption reduced
4.23%
as of 2022
| Content | 2022 | 2023 | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity of urea (thousand tons/year) | 917.77 | 949.13 | Increased 3.42% |
| Gas consumption (GJ/ton urea bag) | 20.205 | 20.116 | Decreased 0.44% |
| Power consumption (GJ/ton urea bag) | 1.659 | 1.697 | Increased 2.34% |
| Total energy consumption (GJ/ton urea bag) | 21.864 | 21.813 | Decreased 0.23% |
Regarding power, we always focus on power saving and promoting effective use of used power, power for production; seeking technology and solutions to take advantage of excess heat, consumable heat to create useful power, promoting energy saving and optimizing the operating circle of the plan. In 2023, energy consumption in manufacturing increased but total energy consumption intensity of Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant reduced by 1.98% as of 2022:
Total energy consumption intensity in 2023 reduced by
1.98%
as of 2022
| Content | Unit | 2022 | 2023 | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total energy consumption | MW/year | 166,734.1 | 170,103.7 | Increased 2.02% |
| Energy consumption intensity | MW/ton of product | 0.1817 | 0.1792 | Decreased 1.35% |
| Energy intensity | GJ/ton of product | 1.633 | 1.611 | Decreased 1.35% |
PVCFC always works out short-term and long-term plans to collect, store and closely control, ensuring compliance with requirements of current law. Overview of waste management in 2024 of PVCFC is as follows:
- Domestic waste: generated from offices, cafeteria, toilets, etc. with a capacity of 112,760kg in 2023 and 110,426kg in 2022. Domestic waste was collected and transferred to Ca Mau Urban Environment JSC for treatment as stipulated
- Ordinary industrial solid waste: wood scraps, broken pallets, plastics, scrap iron, etc. generated with a capacity of 63,288kg in 2023 and 66,752kg in 2022. This waste was collected and transferred to specialized units for treatment as stipulated.
- Hazardous waste: generated with a capacity of 155,714kg in 2023 and 324,926kg in 2022. Hazardous waste was collected and classified at source, stored at hazardous waste warehouse of Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant and transferred to specialized units for treatment as stipulated.
PVCFC understands that business and production activities can have big impacts on biodiversity. Use of fertilizer products causes direct and indirect impacts of biodiversity too. Therefore, apart from doing research and renovation of manufacturing technology, we have also done research on impacts of product use of biodiversity, providing products with positive impacts on environment in general and biodiversity in particular.
Typical projects have been completed and applied: recovery of permeate gas & MP vent gas: gas emissions are directly burned in the environment and converted into fuel to provide heat for production. Moreover, PVCFC has done research on developing new products toward efficiency improvement to reduce greenhouse gas emissions such as N46 plus, Urea BIO. These products will be continuously improved and developed in the future.
In 2023, we have implemented some typical projects including:
- Manufacturing CO₂ in food: making use of recovered gas emissions to increase the amount of CO₂. We have done research to transfer a part of excess CO₂ into CO₂ in food processing. This kind of product helps reduce direct gas emissions and create new products, expanding the company’s activities to new value chains.
- Research on making use of green hydrogen to partially replace hydrogen at Ca Mau Fertilizer Plant: grasping the global trend of energy transition, we have cooperated with partners to conduct research and apply hydrogen production technology by electrolysis technologies to partially replace hydrogen manufactured by current renewable energy.




